Marc Morano, probably first up against the wall, had this post a while back with a number of public threats, from TPM, Joe Romm, Joe Kennedy, Grist Magazine, David Suzuki, and James Hansen, among others.
Yearly Archives: 2009
More on the Climate Pentagon Papers
The Bishop Hill Blog has a summary of a lot of the more interesting emails.
A search engine of the content is here.
John Hinderaker here.
FOIA for Me But Not For Thee
I thought this was one of the more interesting quotes unearthed so far from the Hadley CRU emails:
“When the FOI requests began here, the FOI person said we had to abide by the requests. It took a couple of half hour sessions – one at a screen, to convince them otherwise showing them what CA [Climate Audit] was all about. Once they became aware of the types of people we were dealing with, everyone at UEA (in the registry and in the Environmental Sciences school – the head of school and a few others) became very supportive. I’ve got to know the FOI person quite well and the Chief Librarian – who deals with appeals.”
I am not familiar with the ins and outs of the British FOI request process, but in the US such requests must be honored based on the content of the information requested, and NOT based on the views of the requester or the intended us of the information. Basically, what the FOI officer has determined here is that this was a perfectly legitimate request that had to be honored UNTIL it was learned that it came from a person or group who disagreed with the center’s scientific conclusions and wished to use the data to try to replicate and/or criticize their work — then it could be ignored. In the US, this would be a gross violation of FOIA rules. I am willing to be that it is not too kosher under British law either.
The Real Hockey Stick
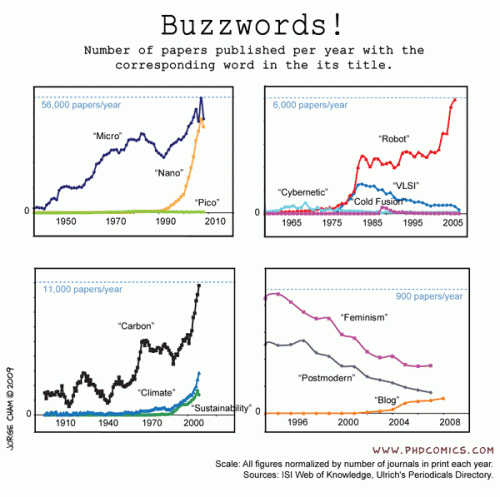
From PHD Comics via Flowing Data, check out the lower left.
Climate Pentagon Papers
An interesting development you have probably seen at other climate sites already (I am pretty conservative about posting this stuff), apparently someone may have hacked the servers at the Hadley Center Climate Research Unit (CRU) in the UK and copied a bunch of data and emails and dropped it into the public realm (via links in a number of site’s comment sections). I downloaded the file but have not checked it out. It is unclear if this is real or a skeptic spoof or even an alarmist-set trap, though initial reactions from the Hadley Center CRU seem to point to it being real. The ethics of the folks who grabbed this material are also seriously in question, though if it turns out to be real I have no problem using the material as it is public / government material that should have been in the public domain anyway (which is why I use the Pentagon Papers analogy).
Andrew Bolt has some background and excerpts from the material. The very first email he has from Phil Jones seems to confirm my suspicions about splicing thermometer data onto proxy series I expressed here. (Update: much more from Steve McIntyre here).
A lot of the stuff in Bolt’s post is really stuff we in the skeptic community already know. RealClimate ruthlessly purges comments of any dissenting or critical voices? Who’d have thunk it.
Climate Presentation Slides
These are the Powerpoint slides for my Nov. 10 presentation in Phoenix.
The slides are available for download at this link (9.9MB): Download ppt
A pdf file of the presentation is here (2.7MB): Download pdf
You can also view a Google docs version of the presentation below, though a bit of the formatting gets screwed up in the translation: Climate Presentation, online viewer
Sign up here to be notified when I post the video
Bummer. I Didn’t Make the List
James Inhofe.
Marc Morano.
Richard Lindzen.
Bjørn Lomborg.
George W. Bush.Names of shame, ignominy, criminals against humanity, against planet Earth itself. Agents of the lethal delays in our response to escalating, accelerating, catastrophic global warming.
Thanks
We had a really good crowd out last night for my lecture. I am currently working on publishing the video and the slides. I am going to destroy the email list for this lecture, but before I do so I am going to send everyone a link to the slides and video when I get them posted. If you would like to be notified when these are up, you may join the email list here.
Posting Drought Over Soon
There is a lot going on that I should be posting about, but I am preparing for a new round of public presentations, of which I give the first tomorrow night in Phoenix. Once that is done, and I can get the video posted, I will be back to normal operations.
By the way, if you like the video, I am available for talks to groups for no speaking fee, if I can get to where you are. My business (totally unrelated to climate) takes me all over the country so I may be near you some time soon. Just drop me an email at the link above.
On the Radio Tonight
For those in Arizona, I will be on the Terry Gilberg show on 550 KFYI talking climate starting at 6:30 or 7:00 to about 8:00.
Reminder: Tuesday, Nov 10 Presentation in Phoenix
If you are in the Phoenix area and interested in a scientific discussion of climate issues, and in particular the science behind the skeptic’s position, you will likely enjoy my lecture this coming Tuesday (Nov 10) in Phoenix. The presentation is free to the public, and will be from 7-9PM in Dorrance Auditorium at the Phoenix Country Day School, on 40th Street just north of Camelback Road. Hope to see you there.
The information web site is here.
The brochure for the presentation is here.
The press release is here.
Good Video
I enjoyed this video from CO2 Science and the Idso family. It has much more in-depth science than most climate videos. For those of you who judge scientific issues based on ad hominem factors, the Idso’s are on ExxonSecret’s S-list, having had the temerity to accept Exxon money at some point in the past. For the rest of you, I think the video is good and worth the price.
Lindzen & Choi
In preparing for my climate presentation in Phoenix next week, I went back and read through Lindzen & Choi, a study whose results I linked here. The study claims to have measured feedback, and have found feedback to temperature changes in the natural climate system to be negative –opposite of the assumption of strong positive feedback in climate models. I found this interesting, as we often do of studies that confirm our own hypotheses.
Re-reading the study, I was uncomfortable with the methodology, but figured I was missing something. Specifically, I didn’t understand how an increase in temperature could result in a decrease in outgoing radiation, as Lindzen says is assumed in all the models. As I have always understood it, the opposite has to be true in a stable system. With an added forcing, temperature increases which increases outgoing radiation until the radiation budget is back in balance. Models that assumed otherwise would have near infinite temepratures. I assumed perhaps that Lindzen & Choi were making measurements during the time the system came back into equilibrium.
Apparently, both Luboš Motl and Roy Spencer have spotted problems as well, and they explain the issue in a more sophisticated way here and here.
But the results I have been getting from the fully coupled ocean-atmosphere (CMIP) model runs that the IPCC depends upon for their global warming predictions do NOT show what Lindzen and Choi found in the AMIP model runs. While the authors found decreases in radiation loss with short-term temperature increases, I find that the CMIP models exhibit an INCREASE in radiative loss with short term warming.
In fact, a radiation increase MUST exist for the climate system to be stable, at least in the long term. Even though some of the CMIP models produce a lot of global warming, all of them are still stable in this regard, with net increases in lost radiation with warming (NOTE: If analyzing the transient CMIP runs where CO2 is increased over long periods of time, one must first remove that radiative forcing in order to see the increase in radiative loss).
So, while I tend to agree with the Lindzen and Choi position that the real climate system is much less sensitive than the IPCC climate models suggest, it is not clear to me that their results actually demonstrate this.
Spencer further makes the point he has made for a couple of years now that feedback is really, really, really hard to measure, because it is so easy to confuse cause and effect.
Spencer by the way points out this admission from the Fourth IPCC report:
“A number of diagnostic tests have been proposed…but few of them have been applied to a majority of the models currently in use. Moreover, it is not yet clear which tests are critical for constraining future projections (of warming). Consequently, a set of model metrics that might be used to narrow the range of plausible climate change feedbacks and climate sensitivity has yet to be developed.”
This is kind of amazing, in effect saying “we have no idea what the feedbacks are or how to measure them, but lacking any knowlege, we are going to consistently and universally assume very high positive feedbacks with feedback factors > 0.7”
Regression Abuse
As I write this, I realize I go a long time without getting to climate. Stick with me, there is an important climate point.
The process goes by a number of names, but multi-variate regression is a mathematical technique (really only made practical by computer processing power) of determining a numerical relationship between one output variable and one or more other input variables.
Regression is absolutely blind to the real world — it only knows numbers. What do I mean by this? Take the famous example of Washington Redskins football and presidential elections:
For nearly three quarters of a century, the Redskins have successfully predicted the outcome of each and every presidential election. It all began in 1933 when the Boston Braves changed their name to the Redskins, and since that time, the result of the team’s final home game before the election has always correctly picked who will lead the nation for the next four years.
And the formula is simple. If the Redskins win, the incumbent wins. If the Redskins lose, the challenger takes office.
Plug all of this into a regression and it would show a direct, predictive correlation between Redskins football and Presidential winners, with a high degree of certainty. But we denizens of the real world would know that this is insane. A meaningless coincidence with absolutely no predictive power.
You won’t often find me whipping out nuggets from my time at the Harvard Business School, because I have not always found a lot of that program to be relevant to my day-to-day business experience. But one thing I do remember is my managerial economics teacher hammering us over and over with one caveat to regression analysis:
Don’t use regression analysis to go on fishing expeditions. Include only the variables you have real-world evidence really affect the output variable to which you are regressing.
Let’s say one wanted to model the historic behavior of Exxon stock. One approach would be to plug in a thousand or so variables that we could find in economics data bases and crank the model up and just see what comes out. This is a fishing expedition. With that many variables, by the math, you are almost bound to get a good fit (one characteristic of regressions is that adding an additional variable, no matter how irrelevant, always improves the fit). And the odds are high you will end up with relationships to variables that look strong but are only coincidental, like the Redskins and elections.
Instead, I was taught to be thoughtful. Interest rates, oil prices, gold prices, and value of the dollar are all sensible inputs to Exxon stock price. But at this point my professor would have a further caveat. He would say that one needs to have an expectation of the sign of the relationship. In other words, I should have a theory in advance not just that oil prices affect Exxon stock price, but whether we expect higher oil prices to increase or decrease Exxon stock price. In this he was echoing my freshman physics professor, who used to always say in the lab — if you are uncertain about the sign of a relationship, then you don’t really understand the process at all.
So lets say we ran the Exxon stock price model expecting higher oil prices to increase Exxon stock price, and our regression result actually showed the opposite, a strong relationship but with the opposite sign – higher oil prices seem to correlate better with lower Exxon stock price. So do we just accept this finding? Do we go out and bet a fortune on it tomorrow? I sure wouldn’t.
No, what we do instead is take this as sign that we don’t know enough and need to research more. Maybe my initial assumption was right, but my data is corrupt. Maybe I was right about the relationship, but in the study period some other more powerful variable was dominating (example – oil prices might have increased during the 1929 stock market crash, but all the oil company stocks were going down for other reasons). It might be there is no relation between oil prices and Exxon stock prices. Or it might be I was wrong, that in fact Exxon is dominated by refining and marketing rather than oil production and actually is worse off with higher oil prices. But all of this points to needed research – I am not going to write an article immediately after my regression results pop out and say “New Study: Exxon stock prices vary inversely with oil prices” without doing more work to study what is going on.
Which brings us to climate (finally!) and temperature proxies. We obviously did not have accurate thermometers measuring temperature in the year 1200, but we would still like to know something about temperatures. One way to do this is to look at certain physical phenomenon, particularly natural processes that result in some sort of annual layers, and try to infer things from these layers. Tree rings are the most common example – tree ring widths can be related to temperature and precipitation and other climate variables, so that by measuring tree ring widths (each of which can be matched to a specific year) we can infer things about climate in past years.
There are problems with tree rings for temperature measurement (not the least of which is that more things than just temperature affect ring width) so scientists search for other “proxies” of temperature. One such proxy are lake sediments in certain northern lakes, which are layered like tree rings. Scientists had a theory that the amount of organic matter in a sediment layer was related to the amount of growth activity in that year, which in term increased with temperature (It is always ironic to me that climate scientists who talk about global warming catastrophe rely on increased growth and life in proxies to measure higher temperature). Because more organic matter reduces x-ray density of samples, an inverse relationship between X-ray density and temperature could be formulated — in this case we will look at the Tiljander study of lake sediments. Here is one core result:
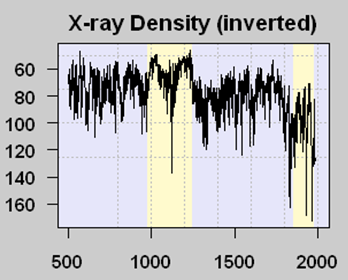
The yellow band with lower X-ray density (meaning higher temperatures by the way the proxy is understood) corresponds pretty well with the Medieval Warm Period that is fairly well documented, at least in Europe (this proxy is from Finland). The big drop in modern times is thought by most (including the original study authors) to be corrupted data, where modern agriculture has disrupted the sediments and what flows into the lake, eliminating its usefulness as a meaningful proxy. It doesn’t mean that temperatures have dropped lately in the area.
But now the interesting part. Michael Mann, among others, used this proxy series (despite the well-know corruption) among a number of others in an attempt to model the last thousand years or so of global temperature history. To simplify what is in fact more complicated, his models regress each proxy series like this against measured temperatures over the last 100 years or so. But look at the last 100 years on this graph. Measured temperatures are going up, so his regression locked onto this proxy and … flipped the sign. In effect, it reversed the proxy. As far as his models are concerned, this proxy is averaged in with values of the opposite sign, like this:
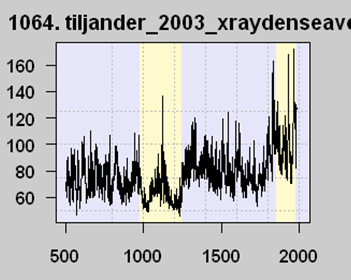
A number of folks, particularly Steve McIntyre, have called Mann on this, saying that he can’t flip the proxy upside down. Mann’s response is that the regression doesn’t care about the sign, and that its all in the math.
Hopefully, after our background exposition, you see the problem. Mann started with a theory that more organic material in lake sediments (as shown by lower x-ray densities) correlated with higher temperatures. But his regression showed the opposite relationship — and he just accepted this, presumably because it yielded the hockey stick shape he wanted. But there is absolutely no physical theory as to why our historic understanding of organic matter deposition in lakes should be reversed, and Mann has not even bothered to provide one. In fact, he says he doesn’t even need to.
This mistake (fraud?) is even more egregious because it is clear that the jump in x-ray values in recent years is due to a spurious signal and corruption of the data. Mann’s algorithm is locking into meaningless noise, and converting it into a “signal” that there is a hockey stick shape to the proxy data.
As McIntyre concludes:
In Mann et al 2008, there is a truly remarkable example of opportunistic after-the-fact sign selection, which, in addition, beautifully illustrates the concept of spurious regression, a concept that seems to baffle signal mining paleoclimatologists.
Postscript: If you want an even more absurd example of this data-mining phenomenon, look no further than Steig’s study of Antarctic temperatures. In the case of proxies, it is possible (though unlikely) that we might really reverse our understanding of how the proxy works based on the regression results. But in Steig, they were taking individual temperature station locations and creating a relationship between them to a synthesized continental temperature number. Steig used regression techniques to weight various thermometers in rolling up the continental measure. But five of the weights were negative!!
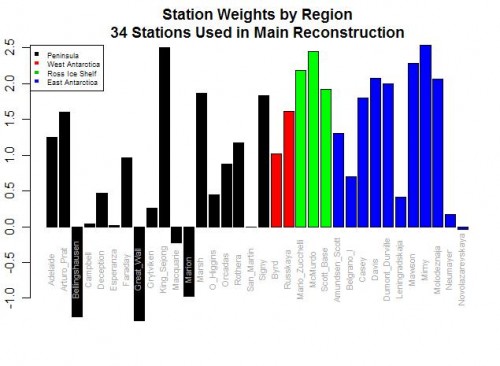
As I wrote then,
Do you see the problem? Five stations actually have negative weights! Basically, this means that in rolling up these stations, these five thermometers were used upside down! Increases in these temperatures in these stations cause the reconstructed continental average to decrease, and vice versa. Of course, this makes zero sense, and is a great example of scientists wallowing in the numbers and forgetting they are supposed to have a physical reality. Michael Mann has been quoted as saying the multi-variable regression analysis doesn’t care as to the orientation (positive or negative) of the correlation. This is literally true, but what he forgets is that while the math may not care, Nature does.
Katrina Victims Have Standing To Sue Over Global Warming
The suit was brought by landowners in Mississippi, who claim that oil and coal companies emitted greenhouse gasses that contributed to global warming that, in turn, caused a rise in sea levels, adding to Hurricane Katrina’s ferocity. (See photo of Bay St. Louis, Miss., after the storm.)
For a nice overview of the ruling, and its significance in the climate change battle, check out this blog post by J. Russell Jackson, a Skadden Arps partner who specializes in mass tort litigation. The post likens the Katrina plaintiffs’ claims, which set out a chain of causation, to the litigation equivalent of “Six Degrees of Kevin Bacon.”
The central question before the Fifth Circuit was whether the plaintiffs had standing, or whether they could demonstrate that their injuries were “fairly traceable” to the defendant’s actions. The defendants predictably assert that the link is “too attenuated.”
But the Fifth Circuit held that at this preliminary stage in the litigation, the plaintiffs had sufficiently detailed their claims to earn a day in court.
I can’t wait to hear the plaintiffs argument as to why U.S. CO2 emissions versus Chinese were the proximate cause of the damage..
I would add that it will be interesting to see how oil companies will be held at fault rather than their customers who actually burned the oil and created the CO2.
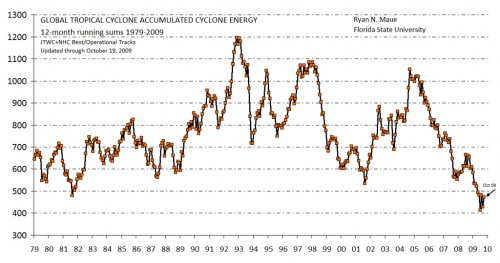
It will also be interesting to see plaintiffs explain this graph of accumulated cyclone energy in the light of their theory that man-made global warming is increasing hurricane strengths and frequencies (ACE is a sort of integration of hurricane and tropical storm strengths over time). (from here via WUWT)
Not Evil Just Wrong Review
I have ordered a copy of “Not Evil Just Wrong” for review. I am excited to see it, but am not going to immediately lend my support until I see the film. There are lots of folks out there who nominally share some of my conclusions but whom I wouldn’t want arguing the case for me. So we’ll see. I will post a review as soon as I have seen it.
Reminder: November 10 Phoenix Climate Presentation
I am making this reminder in honor of Blog Action Day for Climate.
I would like to invite all of you in the Phoenix area to my climate presentation on November 10, 2009. The presentation is timed to coincide with the Copenhagen climate negotiations as Ill as debate on the Boxer cap-and-trade bill in the US Senate.
Despite the explosion of media stories on climate, it is difficult for the average person to really get a handle on the science of greenhouse gasses and climate change in the simplistic and often incomplete or even incorrect popular accounts. This presentation, which is free to the public, will focus on the science of climate change, including:
- Why greenhouse gasses like CO2 warm the Earth.
- How most forecasts of warming from manmade causes are grossly exaggerated, which helps to explain why actual temperatures are undershooting warming forecasts
- How natural processes lead to climate variations that are being falsely interpreted as man-made.
- A discussion of public policy initiatives, and the presentation of a much lower-cost alternative to current cap-and-trade bills
- A review of the role of amateurs in weather and climate measurement, and how the average person can get involved
I have a degree in mechanical and aerospace engineering from Princeton University and a masters degree from Harvard. Most of his training is in control theory and the forecasting of complex dynamic systems, which turn out to be the key failure points in most catastrophic climate forecasts. My mission over the last few years both at this web site and my lectures and debates has been to teach the science of global warming in ways that are accessible to the general public.
Over the years I have preferred a debate format, as for example in my debate with Joe Nation, the author of California’s cap-and-trade law. Unfortunately, the most alarmist proponents of catastrophic manmade global warming have taken Al Gore’s lead and refuse to participate in public debates on the topic. As a result, I will do my best to be fair in presenting the global warming case, and then show which portions are really “settled science” and which portions are exaggerated. You are encouraged to check out Climate-Skeptic.com to see the type of issues I take on – there are links to past presentations, blog posts, books, and even a series of popular and highly-rated YouTube videos.
Below you will also find an example of the types of issues I will discuss. There are many, many folks out there on both sides of this issue whose writing and presentations amount to little more than fevered finger-pointing – I work hard to avoid this type rhetoric and focus on the science.
The presentation will be at 7PM November 10 in the auditorium of the Phoenix Country Day School, just north of Camelback on 40th Street, and is free to the public (this event is paid for me personally and is not sponsored or paid for by any group). The presentation will be about an hour long with another hour for questions and discussion. Folks on all sides of these issues are encouraged to attend and participate in civil discussion of the issues.
If you are interested, please join the mailing list for this presentation to receive reminders and updates:
Example Climate Issue: Positive Feedback
By Warren Meyer
I often make a wager with my audiences. I will bet them that unless they are regular readers of the science-based climate sites, I can tell them something absolutely fundamental about global warming theory they have never heard. What I tell them is this:
Man-made global warming theory is not one theory but in fact two totally separate theories chained together. These two theories are:
- Man-made greenhouse gasses, such as CO2, acting alone will warm the planet betIen 1.0 and 1.5 degrees Celsius by the year 2100.
- The Earth’s climate system is dominated by positive feedbacks, such that the warming from Greenhouse gasses alone is amplified 3-5 or more times. Most of the warming in catastrophic forecasts comes from this second effect, not directly from greenhouse gas warming.
This is not some Iird skeptic’s fantasy. This two-part description of catastrophic global warming theory is right out of the latest IPCC report. Most of the warming in the report’s forecasts actually results from the theory of positive feedback in #2, not from greenhouse gasses directly.
One of the most confusing issues for average people watching the climate debate is how one side can argue so adamantly that the science is “settled” and the other can argue just the opposite. The explanation lies in large part with this two-part theory. There is a high degree of consensus around proposition1, even among skeptics. I may disagree that the warming is 0.8C or 1.2C, but few on the science end of the debate would argue that CO2 has no effect on warming. When people say “the science is settled” they generally want to talk about proposition 1 and avoid discussion of proposition 2.
That is because proposition 2 is far from settled. The notion that a long-term stable system can be dominated by very high positive feedbacks offends the intuition of many natural scientists, who know that most natural processes (short of nuclear fission) are dominated by negative feedbacks. Sure, there are positive feedbacks in climate, just as there are negative feedbacks. The key is how these net out. The direct evidence that the Earth’s climate is dominated by strong net positive feedbacks is at best equivocal, and in fact evidence is growing that negative feedbacks may dominate, thus greatly reducing expected future warming from greenhouse gasses.
In my public presentations, I typically will
- Explain this split of catastrophic man-made global warming theory into two propositions, and how most of the predicted catastrophe comes from the second proposition rather than the first
- Show how skeptics have hurt their credibility by trying to challenge proposition #1
- Explain the mechanics in simple terms of positive and negative feedback
- Show the data and evidence related to feedback
- Show from historic temperature numbers that assumptions of high positive feedback are extremely unlikely to be correct.
I have a video related to these issues of feedback and forecasts on YouTube in a 9 minute video titled “Don’t Panic – Flaws in Catastrophic Global Warming Forecasts.” See all my videos at my YouTube channel.
My Climate Plan
Apparently this is Blog Action Day for Climate. The site encourages posts today on climate that will be aggregated, uh, somehow. Its pretty clear they want alarmist posts and that the site is leftish in orientation (you just have to look at the issues you can check off that interest you — lots of things like “societal entrepreneurship” but nothing on individual liberty or checks on government power). However, they did not explicitly say “no skeptics” — they just want climate posts. So I will take the opportunity today to post a number of blasts from the past, including some old-old ones on Coyote Blog.
From the comments of this post, which wondered why Americans are so opposed to the climate bill when Europeans seem to want even more regulation. Leaving out the difference in subservience to authority between Europeans and Americans, I wrote this in the comments:
I will just say: Because it’s a bad bill. And not because it is unnecessary, though I would tend to argue that way, but for the same reason that people don’t like the health care bill – its a big freaking expensive mess that doesn’t even clearly solve the problem it sets out to attack. Somehow, on climate change, the House has crafted a bill that both is expensive, cumbersome, and does little to really reduce CO2 emissions. All it does successfully is subsidize a bunch of questionable schemes whose investors have good lobbyists.
If you really want to pass a bill, toss the mess in the House out. Do this:
- Implement a carbon tax on fuels. It would need to be high, probably in the range of dollars and not cents per gallon of gas to achieve kinds of reductions that global warming alarmists think are necessary. This is made palatable by the next step….
- Cut payroll taxes by an amount to offset the revenue from #1. Make the whole plan revenue neutral.
- Reevaluate tax levels every 4 years, and increase if necessary to hit scientifically determined targets for CO2 production.
Done. Advantages:
- no loopholes, no exceptions, no lobbyists, no pork. Keep the legislation under a hundred pages.
- Congress lets individuals decide how best to reduce Co2 by steadily increasing the price of carbon. Price signals rather than command and control or bureaucrats do the work. Most liberty-conserving solution
- Progressives are happy – one regressive tax increase is offset by reduction of another regressive tax
- Unemployed are happy – the cost of employing people goes down
- Conservatives are happy – no net tax increase
- Climate skeptics are mostly happy — the cost of the insurance policy against climate change that we suspect is unnecessary is never-the-less made very cheap. I would be willing to accept it on that basis.
- You lose the good feelings of having hard CO2 targets, but if there is anything European cap-and-trade experiments have taught, good feelings is all you get. Hard limits are an illusion. Raise the price of carbon based fuels, people will conserve more and seek substitutes.
- People will freak at higher gas prices, but if cap and trade is going to work, gas prices must rise by an equal amount. Legislators need to develop a spine and stop trying to hide the tax.
- Much, much easier to administer. Already is infrastructure in place to collect fuel excise taxes. The cap and trade bureaucracy would be huge, not to mention the cost to individuals and businesses of a lot of stupid new reporting requirements.
- Gore used to back this, before he took on the job of managing billions of investments in carbon trading firms whose net worth depends on a complex and politically manipulable cap and trade and offset schemes rather than a simple carbon tax.
Payroll taxes are basically a sales tax on labor. I am fairly indifferent in substituting one sales tax for another, and would support this shift, particularly if it heads of much more expensive and dangerous legislation.
Update: Left out plan plank #4: Streamline regulatory approval process for nuclear reactors.
The Single Best Reason Not To Fear a Climate Catastrophe
Apparently this is Blog Action Day for Climate. The site encourages posts today on climate that will be aggregated, uh, somehow. Its pretty clear they want alarmist posts and that the site is leftish in orientation (you just have to look at the issues you can check off that interest you — lots of things like “societal entrepreneurship” but nothing on individual liberty or checks on government power). However, they did not explicitly say “no skeptics” — they just want climate posts. So I will take the opportunity today to post a number of blasts from the past, including some old-old ones on Coyote Blog.
While the science of how CO2 and other greenhouse gases cause warming is fairly well understood, this core process only results in limited, nuisance levels of global warming. Catastrophic warming forecasts depend on added elements, particularly the assumption that the climate is dominated by strong positive feedbacks, where the science is MUCH weaker. This video explores these issues and explains why most catastrophic warming forecasts are probably greatly exaggerated.
You can also access the YouTube video here, or you can access a higher quality version on Google video here.
If you have the bandwidth, you can download a much higher quality version by right-clicking either of the links below:
- 640 x 480 Windows media version, 86MB
- 320 x 240 Windows media version, 31MB
- Quicktime 640 x 480 version, 245MB
I am not sure why the quicktime version is so porky. In addition, the sound is not great in the quicktime version, so use the windows media wmv files if you can. I will try to reprocess it tonight. All of these files for download are much more readable than the YouTube version (memo to self: use larger font next time!)
By Popular Demand…
I have gotten something like 6 zillion emails asking that I link the Paul Hudson’s BBC News article “What happened to Global Warming.” Frequent readers of this and other science-based skeptic sites won’t find much new here, except the fact that is appeared on the BBC. Apparently it is now the most read article on the BBC site.